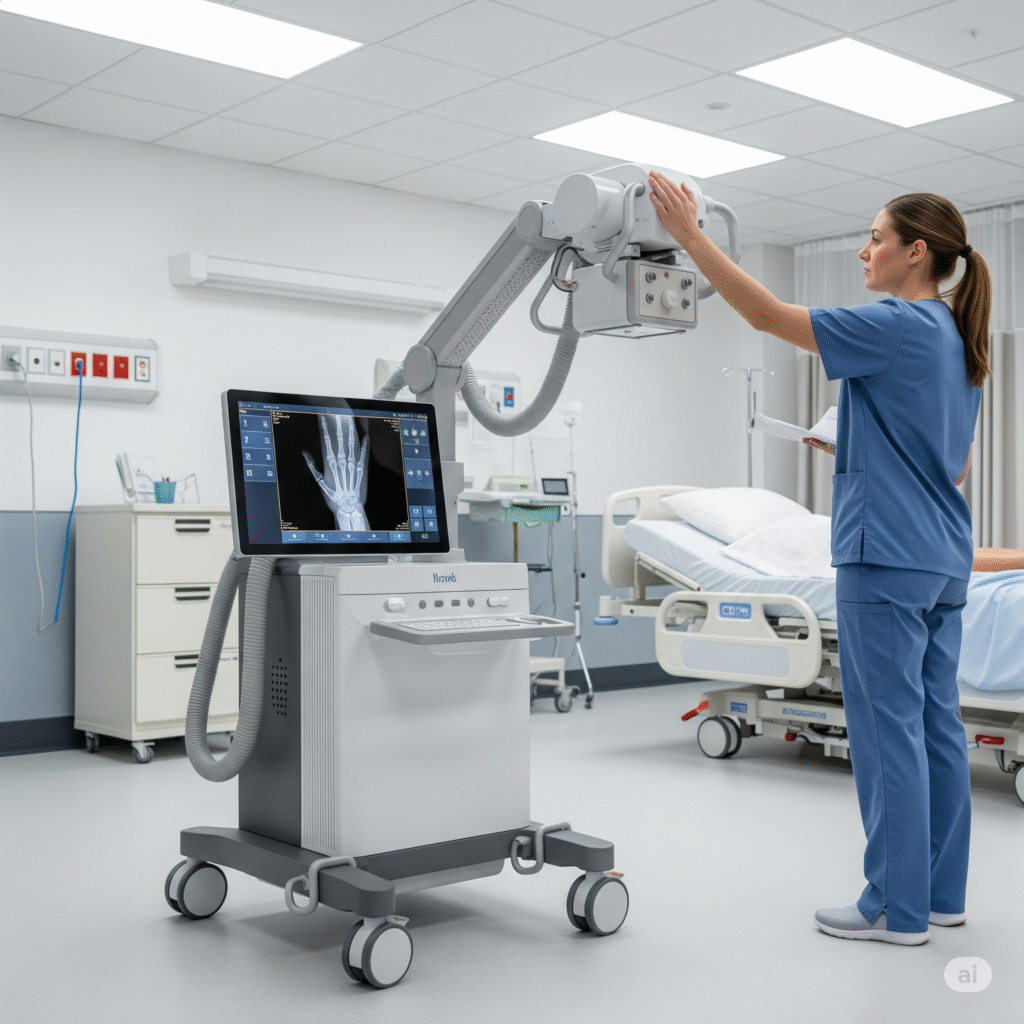
Faster diagnosis at the point of care: ERs, ICUs, ambulances, rural clinics, and home care.
In the fast-paced environment of healthcare, diagnostic speed can be the difference between a life saved and a life lost. Traditional X-ray imaging requires moving patients to designated imaging rooms—often risky and time-consuming for critical cases. Portable X-ray machines bring high-quality imaging to the patient, enabling timely decisions in emergency wards, ICUs, rural clinics, and even homes.
What Are Portable X-Ray Machines?
Portable or mobile X-ray units are compact systems designed to capture radiographic images at the point of care. Modern systems pair a mobile X-ray generator with a digital radiography (DR) detector for fast image acquisition and instant review.
Advantages
- Time Efficiency: No need to transfer critically ill or immobile patients; imaging happens bedside.
- Cost Reduction: Lower infrastructure and staffing needs vs. fixed imaging rooms for many use cases.
- Accessibility: Enables imaging in remote locations and during transport (ambulances, field units).
Key Use Cases
From confirming line placements and chest conditions to trauma screening and post-operative checks, portable X-ray supports rapid, repeatable imaging without patient movement.
Impact on Rural Healthcare
Portable X-ray units bridge the urban–rural care gap by delivering instant imaging where fixed facilities are scarce. The result: earlier detection, faster treatment initiation, fewer referrals, and lower out-of-pocket costs for patients. Tele-radiology workflows let clinicians share images with specialists for quick reads, improving outcomes and continuity of care.
How Portable X-Ray Works (At a Glance)
- Position & Prep: Position patient; set exposure parameters based on anatomy.
- Exposure: X-ray generator emits radiation; DR panel captures the image.
- Review: Image appears instantly on the console for QA and basic measurements.
- Share: Images are exported to PACS/Cloud or sent via DICOM for reporting—on-site or via tele-radiology.
Choosing the Right Portable X-Ray: A Quick Buying Guide
Evaluate these factors before purchase:
- Power Output (kW) & mAs: Ensure adequate penetration for chest/abdomen/orthopedic studies.
- Detector Type: DR (flat-panel) for speed and dose efficiency; check detector size & ruggedness.
- Battery & Mobility: Battery life, charge time, total weight, wheels, and maneuverability in tight spaces.
- Workflow & Connectivity: DICOM, PACS/Cloud, Wi-Fi, on-board workstation, image stitching options.
- Radiation Safety: Collimation, exposure indicators, integrated dose tracking, ALARA support.
- Compliance: Look for MDR/CDSCO registration (India), ISO 13485; consider CE/FDA where applicable.
- Service & Warranty: On-site support, spare parts availability, calibration, and uptime SLAs.
Safety & Best Practices
- Follow ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) principles; use shielding and proper collimation.
- Provide PPE (lead aprons/thyroid shields) and maintain exposure logs and dosimetry.
- Train staff on positioning, exposure settings, and equipment handling to minimize retakes.
Quick FAQ
Q: Are portable X-ray images as good as fixed room images?
A: For many exams (e.g., chest, extremities), modern DR-based portable systems provide diagnostic quality comparable to fixed rooms—when properly operated.
Q: Can these be used in ambulances and remote camps?
A: Yes. Battery-powered units with rugged DR panels are suited for ambulances, field clinics, and outreach programs.
Q: What about maintenance?
A: Schedule periodic calibration, detector care, and software updates; ensure vendor provides responsive on-site service.
